In our previous blog we have seen uploading, deleting and fetching OCI Object Storage file using APEX_WEBSERVICE API. If you’re using Oracle Autonomous Database, you can directly use the DBMS_CLOUD package to interact with your OCI Buckets — no need to manually handle HTTP headers or web credentials.
In this article, we will guide you on how to upload, download, and delete files from an OCI bucket using DBMS_CLOUD.
Prerequisites
- Oracle Autonomous Database (ATP/ADW)
- DBMS_CLOUD access granted
- OCI Account with Object Storage bucket created
- Auth token for the OCI user
Step 1: Setup Credentials Using
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL
We first need to create credentials for accessing the OCI Object Storage.
Example:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED_2',
username => 'your_email@example.com',
password => 'your_oci_auth_token'
);
END;- Username is your OCI user login (usually your email)
- Password is the OCI Auth Token, not your normal password
🔐 Generate this from: OCI Console → Identity → Users → Auth Tokens
Step 2: Upload File to OCI Bucket
Upload Example:
DECLARE
l_blob BLOB;
l_clob CLOB := 'This is a sample text file generated in PL/SQL.';
l_dest_off INTEGER := 1;
l_src_off INTEGER := 1;
l_lang_ctx INTEGER := DBMS_LOB.DEFAULT_LANG_CTX;
l_warning INTEGER;
BEGIN
-- Initialize a temporary CLOB and BLOB
DBMS_LOB.CREATETEMPORARY(l_blob, TRUE);
-- Convert CLOB to BLOB
DBMS_LOB.CONVERTTOBLOB(
dest_lob => l_blob,
src_clob => l_clob,
amount => DBMS_LOB.LOBMAXSIZE,
dest_offset => l_dest_off,
src_offset => l_src_off,
blob_csid => DBMS_LOB.DEFAULT_CSID,
lang_context => l_lang_ctx,
warning => l_warning
);
DBMS_CLOUD.PUT_OBJECT (
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED_2',
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.ap-mumbai-1.oraclecloud.com/n/your_namespace/b/your_bucket/o/test1.txt',
contents => l_blob
);
DBMS_LOB.FREETEMPORARY(l_blob);
end;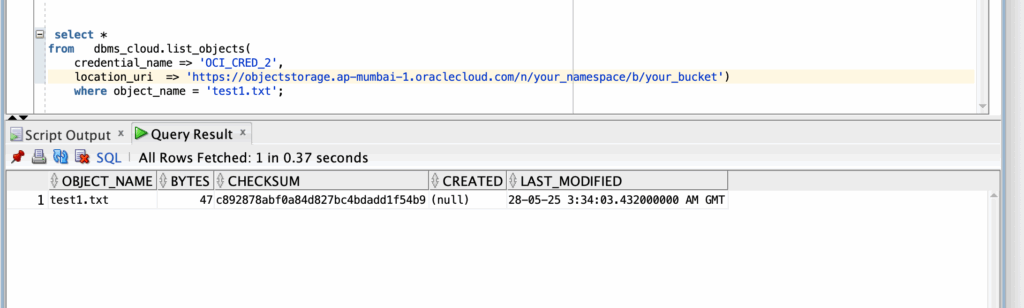
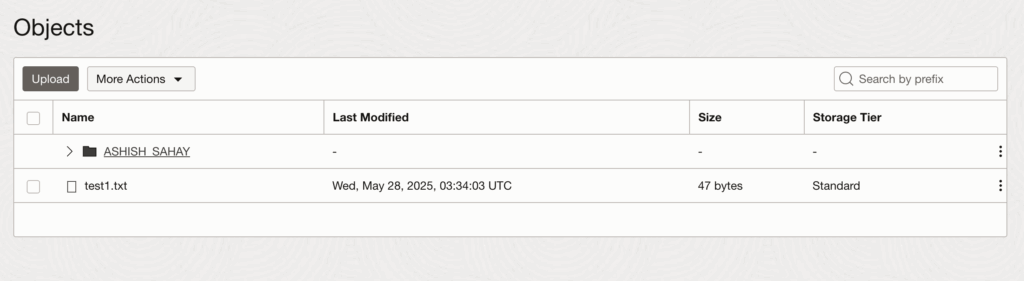
Best Practices:
- Make sure object_uri contains the full bucket URL
- file_name can refer to a table/column or an accessible directory (in ATP, APEX files are accessible)
Step 3: Download File from OCI Bucket
You can download the file from OCI to a local directory or directly stream via URL in APEX.
Download File (Copy to Directory):
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT(
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED_2',
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.ap-mumbai-1.oraclecloud.com/p/your_namespace/b/your_bucket/o/test1.txt',
directory_name => 'your_directory_name',
file_name => 'test1.txt' -- local directory in ATP
);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('File downloaded successfully!');
END;📥 Save to table
declare
l_blob blob;
begin
l_blob := dbms_cloud.get_object (
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED_2',
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.ap-mumbai-1.oraclecloud.com/p/your_namespace/b/your_bucket/test1.txt');
---Insert into your local table
end;
/Step 4: Delete File from OCI Bucket
Use DBMS_CLOUD.DELETE_OBJECT to remove files.
Delete File Example:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.DELETE_OBJECT(
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED_2',
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.ap-mumbai-1.oraclecloud.com/p/your_namespace/b/your_bucket/o/test1.txt'
);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('File deleted successfully!');
END;Summary
Using DBMS_CLOUD in Oracle Autonomous Database is the easiest and most secure way to interact with OCI Object Storage in your APEX application.
✨ No need to manage REST headers or encode URLs manually!
📩 Need expert help in integrating APEX with OCI?
Contact us at contact@ontoorsolutions.com
#orclapex #OracleAPEX #DBMSCLOUD #OCI #AutonomousDB #OntoorSolutions
